polarimeter s enantiomer|automatic polarimeter : mfg Polarimetry. updated. Most physical properties of enantiomers i.e., melting point, . webAcompanhantes em Paragominas. Brasil. Pará. Paragominas. Escort puro carisma, simpática, atenciosa e comunicativa. Paragominas 30 anos R$ 200. Acompanhante .
{plog:ftitle_list}
ground-floor n as adj (storey: at ground level) en rez-de-chaussée, au rez-de-chaussée loc adv: Note: In US English this level is usually called the first floor, but it is sometimes called the ground floor. Brian lived in a ground-floor flat. Brian vivait dans un appartement au (or: en) rez-de-chaussée.
Since the pure S enantiomer ((+) 61 o) is dextrorotatory (positive, clockwise), the R enantiomer must be levorotatory. The observed rotation of the mixture is levorotatory since its negative .
The ratio, the purity, and the concentration of two enantiomers can be measured via polarimetry. Enantiomers are characterized by their property to rotate the plane of linear polarized light. Therefore, those compounds are called optically active and their property is referred to as optical rotation. Light sources such as a light bulb, Tungsten Halogen, or the sun emit electromagnetic waves at the frequency of visible light. Their electric field oscillates in all possible planes relativ. Polarimetry. updated. Most physical properties of enantiomers i.e., melting point, .
Optical activity is measured by a polarimeter, and is dependent on several factors: concentration of the sample, temperature, length of the sample tube or cell, and wavelength of the light passing through the sample. . Draw .A solution containing 0.08 g/mL of a pure R enantiomer in a 1 dm colorimeter rotates plane polarized light by +4 What is the specific rotation of the S enantiomer? How mu Ch of the R enantiomer is present in 10 g of a mixture which has an enantiomer excess of 30 % of the S .
The polarimeter is an instrument that measures the direction and angles of rotation of plane-polarized light. . It was not recognized at that time that only the R-enantiomer has the antiemetic property, while the S-enantiomer was a .Question: A solution containing 0.08 g/ml of a pure R enantiomer in a 1 dm polarimeter cell rotates plane polarized light by +4 degree. What is the specific rotation of the S enantiomer? Show transcribed image text. There are 3 steps to solve this one. Solution.A solution containing 0.4 g/mL of a pure S enantiomer is a 1 dm polarimeter rotates plane polarized light by +5.6°. What is the rotation of a solution containing 0.8 g/mL of the S enantiomer in the same polarimeter?. I. +5.6. II. +11.2. III. +2.8. IV. +1.4 An easily constructed and inexpensive polarimeter with an optical rotation angle resolution of about 0.5° is presented. It is made from small pieces of polarizing film, 2 LEDs, a protractor, and a few wires, all held in place with plastic interlocking toy bricks, such as Lego bricks. The instrument was used to demonstrate the optical rotation of plane polarized light as .
A solution of a pure enantiomer is circularly birefringent. In contrast, an equimolar mixture of two enantiomers will have an equal number of refractions to the right and left, and the net result will be α=0. Thus, a polarimeter cannot distinguish an achiral compound from a racemate.
A mixture of two enantiomers with a composition of 65.0% R has an observed rotation of 25.3 degrees in a 10.0 cm polarimeter tube. If the mixture has a concentration of 2.038 g/mL at 25 degrees C, what is the predicted [α] 25 D of an optically pure sample of the S enantiomer?A polarimeter is a device that measures the rotation of linearly polarized light by an optically active sample. This is of interest to organic chemists because it enables differentiation between optically active stereoisomers, i.e., enantiomers. Enantiomers, chiral molecules, are molecules which lack an internal plane of symmetry and have a non-superimosable mirror image. One . Upon crystallization, the [S,S] and [R,R] enantiomers gave different crystals which Pasteur separated mechanically, i.e. by hand. [Note: in the figure below, we show “tartaric acids”; Pasteur did his work on the salts of the conjugate bases, which we call “tartrates”] . Here is a diagram of a modern polarimeter. Image source: wikipedia
23) A solution containing 0.4 g/mL of a pure S enantiomer is a 1 dm polarimeter rotates plane polarized light by +5.6°. What is the rotation of a solution containing 0.8 g/mL of the S enantiomer in the same polarimeter?
2. A solution of 0.1 g/mL of a pure R enantiomer in a 1.0 dm (i.e., 10 cm) polarimeter rotates plane polarized light by +4.8°. What is the rotation observed on this solution in a 2 dm polarimeter? a) +2.4° b) +4.8° c) +19° d) +9.6° View AnswerQuestion: A solution containing 0.04 g/mL of a pure S enantiomer in a 1 dm polarimeter rotates plane polarized light by +2°. What is the specific rotation of the R isomer? Question 17 options: -50° -20° +10° +50°Question: 17. A solution containing 0.4 g/mL of a pure S enantiomer in a 1 dm polarimeter rotates plane polarized light by +5.6. What is the rotation of a solution containing 0.8 g/mL of the Renantiomer in the same polarimeter. A1+2.8" B)-5g" C)+11.2° D)-56" E)-11.2°The instrument with which optically active compounds are studied is a polarimeter, shown in the figure below. . It is the (S) enantiomer because of its structure and the (-) enantiomer because samples of the enantiomer with .
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.Answer to 6. If you had the two enantiomers of carvone in. Science; Chemistry; Chemistry questions and answers; 6. If you had the two enantiomers of carvone in separate, unmarked bottles, could you use just your nose and a polarimeter to determine: whether it is the (+) or (−) enantiomer that smells like spearmint?A polarimeter is an optical instrument for accurately measuring the angle by which the polarization direction of light is rotated in an optically active medium. . i.e., the two enantiomers rotate the polarization direction in different directions, and the angular rotation contributions from both enantiomers simply add up – for example to .
testing voltage drop across a wire
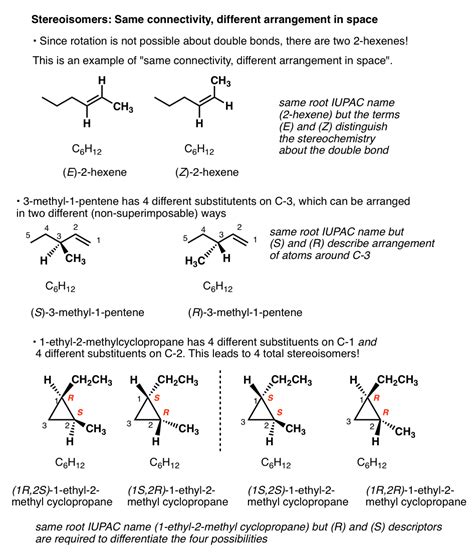
For example 2-butanol, which possess a chiral center (one carbon bound to four different ligands). Figure 1 illustrates that 2-butanol exists as two mirror-image isomers, or enantiomers. The atomic connectivity in the S-isomer is identical to that of its mirror-image R-isomer, except that two of the groups attached to carbon were interchanged.A mixture of two enantiomers with a composition of 65.0%R has an observed rotation of −25.3∘ in a 10.0 cm polarimeter tube. If the mixture has a concentration of 2.038 g/mL at 25∘C, what is the predicted [a]25∘ of an optically pure sample of the S enantiomer? (4 points)The mirror images are called left- and right-handed enantiomers. Chiral molecules are typically organic molecules and biomolecules, such as sugars, starch, flavors, and essential oils, active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), amino acids, and various other biomolecules. . A polarimeter is an instrument which measures the angle of rotation by .A polarimeter is an instrument that allows polarized light to travel through a sample tube containing an organic compound and the degree to which an organic compound rotates plane-polarized light is measured. . while the S-enantiomer was a teratogen that causes congenital deformations. The drug was marketed as a racemic mixture and caused .
The optical activity of enantiomers and their specific rotations can be measured with the help of an instrument called polarimeter. The four main components of this device are: the light source . Laurent’s Half-Shade Polarimeter is an optical instrument used to measure the optical rotation of substances, typically liquid solutions containing optically active compounds. These compounds have the ability to rotate the plane of polarization of linearly polarized light, a property that can be exploited to determine the concentration, purity, or specific rotation of the .a) What mass of (S)-(-)-mandelic acid is present in a 10 g sample which has an enantiomeric excess of 20% of the S-enantiomer? b) The specific rotation of the S-enantiomer of a compound is -120^\circ. What is the enantiomeric excess of a sample of the c; Suppose you are given a sample of a homogeneous liquid.
A mixture of two enantiomers with a composition of 65.0% R has an observed rotation of -25.3° in a 10.0 cm polarimeter tube. If the mixture has a concentration of 2.038 g/mL at 25°C, what is the predicted specific rotation ([alpha] 25 D) of an optically pure sample of the S enantiomer? Then, cholesterol esterase is used to hydrolyse the (S)-enantiomer of the ester, which precipitates from solution. The (R)-enantiomer can be obtained after the workup of the mother liquors. . In order to prove the optical purity, the optical rotation can be determine using a polarimeter. In chem 30CL, currently GC on a chiral column is used .
stereoisomeric pair enantiomers
WEBRESULTADO DE EXAMES. Para acessar os resultados dos exames, digite o Número do protocolo e clique em Consultar. Caso ocorra algum problema na visualização de laudos e imagens ou seja necessário recuperar o número de protocolo, entre em contato através dos contatos: . . . . | [email protected]. Laudos.
polarimeter s enantiomer|automatic polarimeter